An introduction to Skyshelves
Glass windows or walls are used in buildings in order to increase the beauty of the building and to bring sunlight into the building. Ironically, binds are used to cover the glass and obstruct the sunlight.
Problems with normal glass
The below images depict the common problems with normal glass.
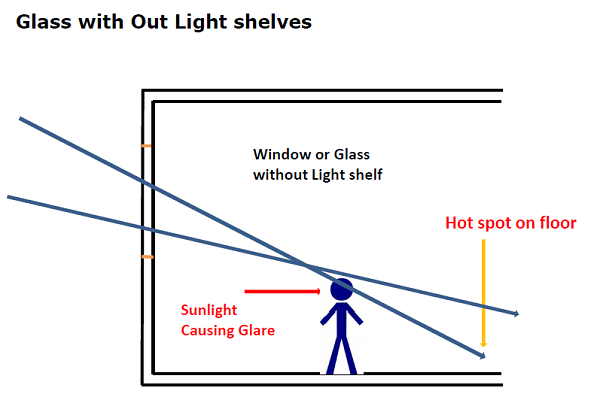
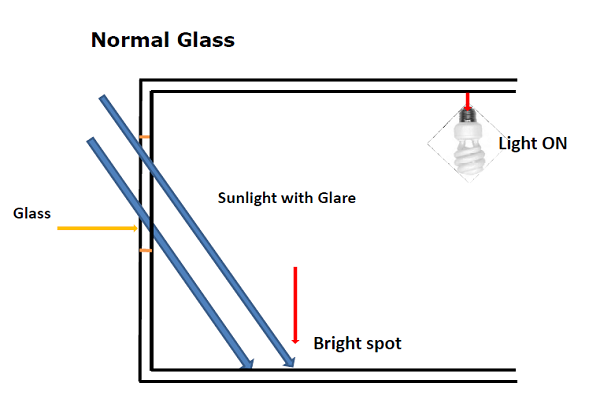
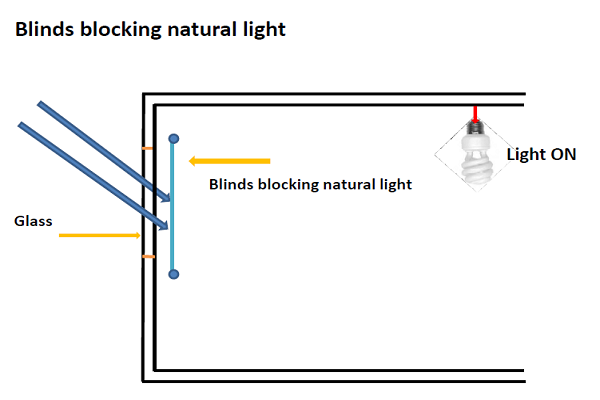






Some common problems that can be inferred from the above images are
- Heat buildup due to the formation of hot spots
- Blinds has to be used additionally to prevent the sunlight coming inside.
- In spite of having a glass window that allows natural sunlight inside, it is blocked and the electrical lights are used in the daytime.
- Radiant Heat gain
- Non uniform lighting
Skyshelves
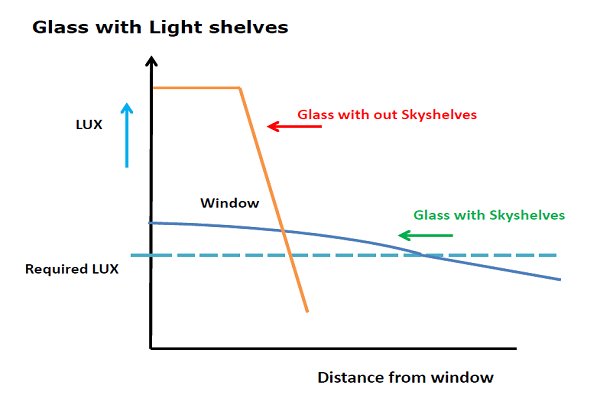
The use of skyshelves daylights helps to overcome this shortfall. It eliminates the glare, but at the same time, penetrates the sunlight deep into the building. This eliminates the heat and glare while providing natural sunlight into the building. This reduces the use of electrical lights inside the building. Since the use of electrical lights is eliminated, the heat build up inside the building is also avoided. This reduces the air conditioner’s load to a great extent. Overall, the use of skyshelves reduce the power consumption.
Types of Skyshelves
Skyshelves are of two types
- Day Glazing
- Vision Glazing
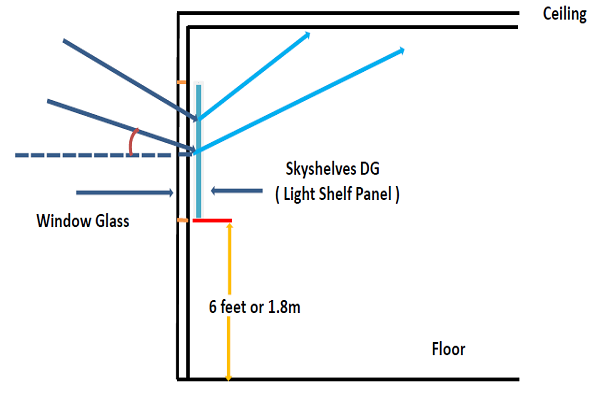
Skyshelves Day Glazing
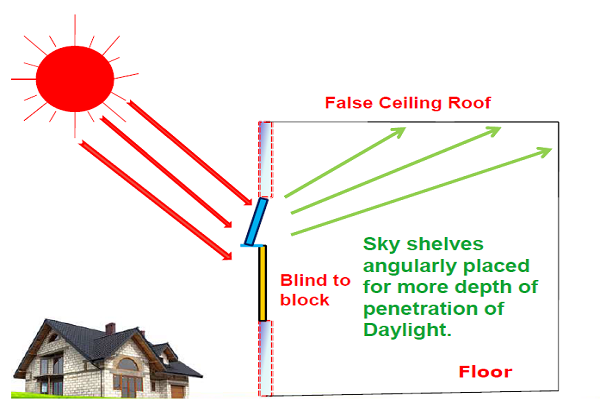
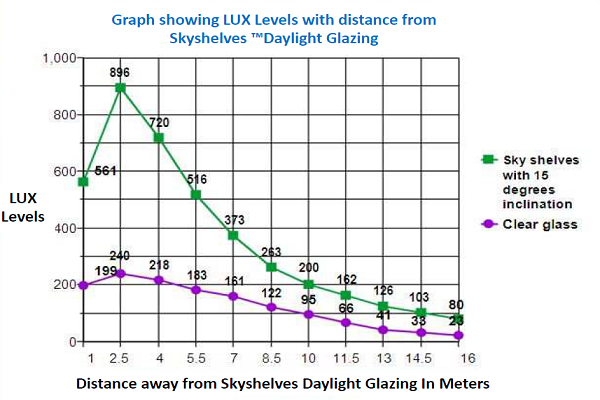
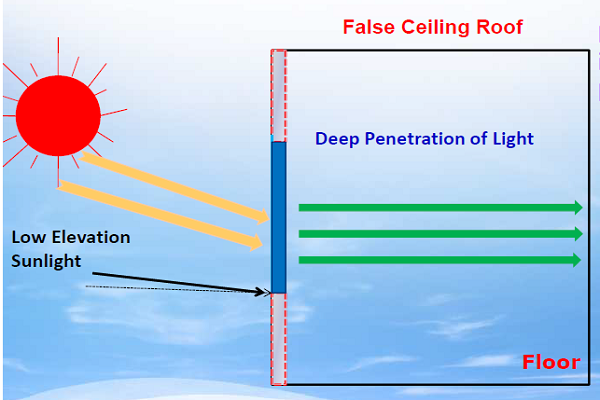
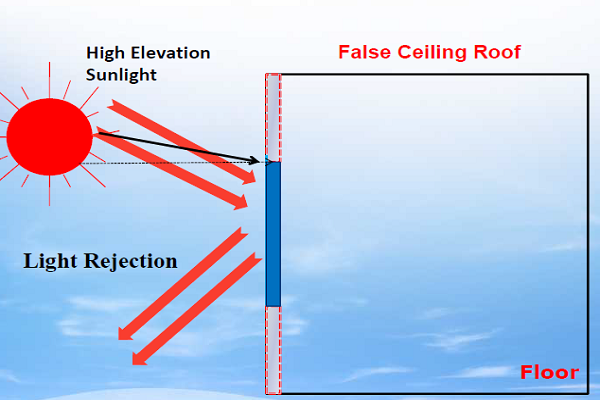
Day glazing is a panel of glass placed below the roof on the walls to redirect the sunlight onto the roof of the buildings. Since most of the roofs are white in color, the sunlight is reflected on the floor, thereby increasing the lighting of the floor area. The day glazing brings sunlight in to the building and avoids the heat buildup. The below images depict the working of day glazing.


| Glazing | U Value | SHGC |
| Single Glazed | 5.0 w/sq.m. k | 0.7 |
| Double Glazed | 2.8 w/sq.m. k | 0.6 |
Glass Specification: 5 mm clear with 12mm air gap;
U Value – U Value is the rate of heat transfer through a structure divided by the difference in temperature across structure.
SHGC – Solar Heat Gain Coefficient is the fraction of incident solar radiation admitted through a window, both directly transmitted and absorbed and subsequently released inward. It is expressed between 0 and 1.
Application images



Cost Benefit Calculations
Assumptions
| Room Floor Area | 100 Sq.m. |
| Required Illumination | 300 lux |
| Roof Reflectivity | 80% |
| Skyshelves Light Transmission | 65% |
| Lumen required by 100 Sq.m. room floor area | 1,20,000 lumen |
Facts
| Day Glazing Skyshelves required to produce 1,20,000 lumens | 2.5 Sq.m. |
| Electrical light required to light up 100 Sq.m. area (at 80 lm per watt) | 1.5 KW |
| Energy Saving at 9 hours usage a day at an unit electricity cost of Rs. 8 for 300 days | 1.5 x 9 x 8 x 300 = Rs. 32,400 per annum |
| Cost of 2.5Sq.m Day Glazing Skyshelves | Rs. 20,000 |
| Return on Investment | 7.5 months |
| Other Benefits | Savings in Air Condition cost (no heat build up due to switching off of electrical lights) |
Advantages of Day Glazing
- Building spaces get bright daylight
- Uniform illumination
- Savings in electricity cost
- Delivers light even in diffused lighting conditions
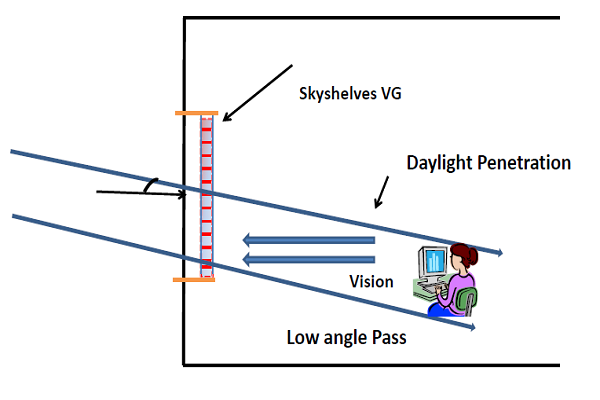
Skyshelves Vision Glazing
Skyshelves vision glazing increases the daylighting inside the building and reduces the need for electrical lights. It provides an excellent choice for architects and builders to balance light and heat of sunlight.



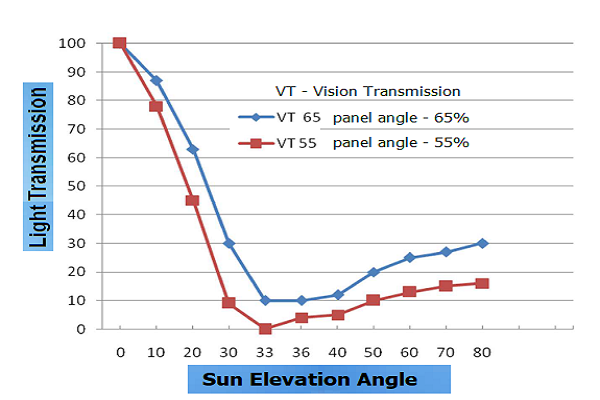
| Sun elevation angle | SHGC | U Value | Vision Transmission |
| 0 | 0.6 | 2.5w / sq.m. K | 65% |
| 40° – 60° | 0.2 | – |
Glass Specification: 5 mm clear with 12mm air gap;
U Value – U Value is the rate of heat transfer through a structure divided by the difference in temperature across structure.
SHGC – Solar Heat Gain Coefficient is the fraction of incident solar radiation admitted through a window, both directly transmitted and absorbed and subsequently released inward. It is expressed between 0 and 1.
Skyshelves Vision Glazing Application Images
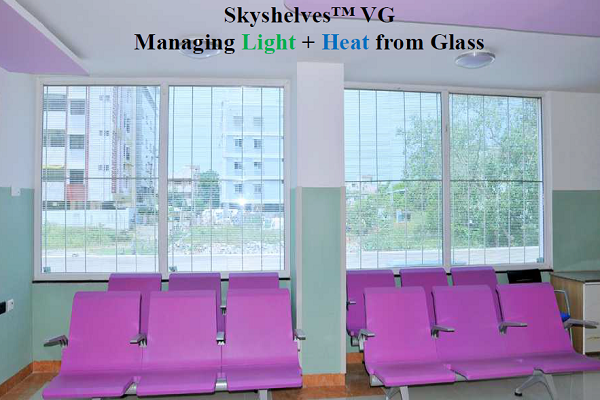




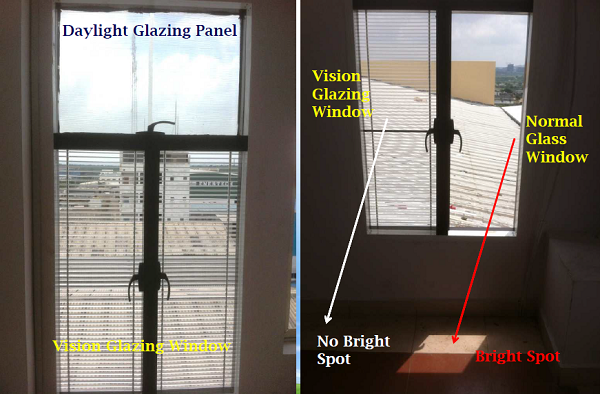


Features and Benefits of Vision Glazing
- No use of blinds, both internal and external leading to cost saving
- It cuts off glare and heat gains resulting energy saving
- Provides diffused daylights, thus helping to reduce enegry
- Reduces air conditioner’s operational cost
- Provides good vision tranmission